Build A Simple Banking System in C++
I am going to use this post to recap what I have done to solve a coding challenge - building a simple banking system in C++. This exercise originates from one online course authored by Abdul Bari Mohammed.
Here is the flowchart of our program.
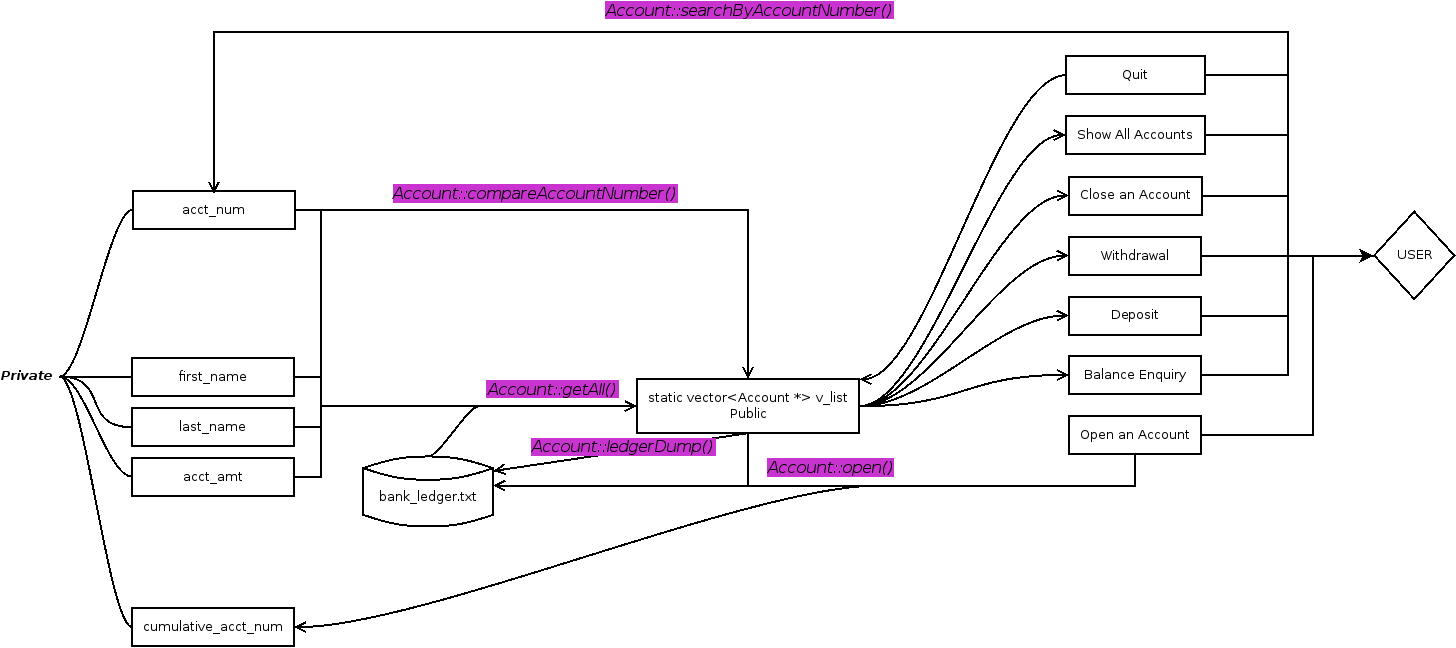
This “ugly” yet simple flowchart is made by Dia , in case you wonder.
We are going to create three files: main.cpp, Account.h and Account.cpp.
main.cpp
The main.cpp basically contains the menu and makes the function call when
the user selects the option. First, let us include the essentials and take
care of the namespace.
// main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include "Account.h"
using std::cout;
using std::cin;
using std::endl;
using std::vector;
Here comes our main(). We need to declare and initialize an integer variable
option to 0, then declare a const pointer pointing to the address of the
variable option.
// main.cpp
...
int main() {
int option = 0;
int *const option_ptr = &option;
...
Now, we can use the classic switch / case flow control to handle the
menu part. For each menu option, we will create a static class member
function and reduce the “clunkiness” in our main.cpp. In case 7, we
use an vector iterator to delete our user-defined class Account pointers
in the heap memory before exiting the program. We will discuss this more
in the later session.
// main.cpp
...
cout << "\n*WELCOME TO BANKING SYSTEM*" << endl;
while (*option_ptr != 7) {
cout << "\nSelect one option below: "
<< "\n1. Open an Account"
<< "\n2. Balance Enquiry"
<< "\n3. Deposit"
<< "\n4. Withdrawal"
<< "\n5. Close an Account"
<< "\n6. Show All Accounts"
<< "\n7. Quit" << endl;
cin >> *option_ptr;
switch (*option_ptr) {
case 1:
Account::open();
break;
case 2:
Account::balance();
break;
case 3:
Account::deposit();
break;
case 4:
Account::withdraw();
break;
case 5:
Account::close();
break;
case 6:
Account::showAll();
break;
case 7: {
Account::ledgerDump();
// Delete all vector pointers.
vector<Account *>::iterator itr;
for (itr = Account::v_list.begin(); itr != Account::v_list.end(); itr++) {
delete *itr;
}
cout << "We hope to see you soon! Bye!" << endl;
break;
}
default:
cout << "*Please enter a valid option (1~7)*" << endl;
break;
}
}
...
Again, do not forget to delete the pointer for the best practice.
// main.cpp
...
delete option_ptr;
return 0;
...
Account.h
Next, let us work on Account.h. We create 5 data members in private.
// Account.h
...
#include <vector>
#include <string>
using std::vector;
using std::string;
using std::ifstream;
using std::ofstream;
using std::ostream;
class Account {
private:
static long cumulative_acct_num;
long acct_num;
mutable string first_name;
mutable string last_name;
mutable long acct_amt;
...
Notice, the mutable allows our data members to be customizable even in
const class member functions.
In public section, we need a static vector of class Account pointers,
v_list. This vector is populated as we start the program, and stores
all updated account information during runtime. Finally, this vector will
be dumped back to the text file bank_ledger.txt on the hard drive.
// Account.h
...
public:
static vector<Account *> v_list;
...
Further, we create constructors, mutators and accessors.
// Account.h
...
Account(string first_name, string last_name, const long &acct_amt);
Account(const long &account_num, string first_name, string last_name, const long &acct_amt);
Account() : Account(getAccountNumber(), "", "", 0L) {};
Account(const Account &a);
void setFirstName(const string &fn) const;
void setLastName(const string &ln) const;
void setAccountAmount(const long &account_amt) const;
const long &getAccountNumber() const;
const string &getFirstName() const;
const string &getLastName() const;
const long &getAccountAmount() const;
static long getLastAccountNumber(); // Retrieve account info and get the latest account number
static vector<Account *> getAll();
...
We also need file input, output and insertion operator overloading.
// Account.h
...
friend const ifstream &operator>>(ifstream &ifs, vector<Account *> &v_list);
friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &out, const Account &a);
friend const ofstream &operator<<(ofstream &ofs, const Account &a);
...
Here comes our facilitators. We will have more detailed discussion about
them in Account.cpp.
// Account.h
...
static void open();
static bool compareAccountNumber(const Account *acct_ptr, const long &acct_num) {
return (*acct_ptr).getAccountNumber() == acct_num;
}
static Account *searchByAccountNumber(const long &acct_num);
static void balance();
static void ledgerDump();
static void deposit();
static void withdraw();
static void close();
static void showAll();
...
Last but not the least, we create the destructor.
// Account.h
...
~Account();
};
...
Account.cpp
We start this file by creating a few lines first.
// Account.cpp
...
#include "Account.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using std::endl;
using std::cout;
using std::cin;
using std::ios;
using std::vector;
using std::ifstream;
using std::ofstream;
using std::string;
using std::ostream;
vector<Account *> Account::v_list = Account::getAll(); // Get all account info
long Account::cumulative_acct_num = Account::getLastAccountNumber(); // Get the latest account number
...
As discussed earlier, the program loads v_list with current account
information in bank_ledger.txt by using a static class member function
getAll(). Similarly, cumulative_acct_num stores the latest account
number by calling another class member function getLastAccountNumber().
What comes next are constructors, mutators and accessors. We use member initialization list instead of assignment in the constructors.
// Account.cpp
...
Account::Account(string first_name, string last_name, const long &acct_amt) :
first_name(std::move(first_name)),
last_name(std::move(last_name)),
acct_amt(acct_amt),
acct_num(++cumulative_acct_num) {
}
Account::Account(const long &account_num, string first_name, string last_name, const long &acct_amt) :
first_name(std::move(first_name)),
last_name(std::move(last_name)),
acct_amt(acct_amt),
acct_num(account_num) {
}
Account::Account(const Account &a) :
first_name(a.getFirstName()),
last_name(a.getLastName()),
acct_amt(a.getAccountAmount()),
acct_num(++cumulative_acct_num) {
}
...
Here are the mutators.
// Account.cpp
...
void Account::setFirstName(const string &fn) const {
this->first_name = fn;
}
void Account::setLastName(const string &ln) const {
this->last_name = ln;
}
void Account::setAccountAmount(const long &account_amt) const {
this->acct_amt = account_amt;
}
...
And the accessors:
// Account.cpp
...
const long &Account::getAccountNumber() const {
return acct_num;
}
const string &Account::getFirstName() const {
return first_name;
}
const string &Account::getLastName() const {
return last_name;
}
const long &Account::getAccountAmount() const {
return acct_amt;
}
vector<Account *> Account::getAll() {
vector<Account *> list;
ifstream ifs;
ifs.open("bank_ledger.txt");
if (!ifs)
return {};
// Load all account info to a vector of Account class pointers
while (!ifs.eof())
ifs >> list;
return list;
}
long Account::getLastAccountNumber() {
// Return the latest account number in the vector
return Account::v_list.empty() ? 0 : (*Account::v_list.back()).getAccountNumber();
}
...
As to the facilitators, most of them are static class member functions and
are used primarily for each menu option in main.cpp. Here is what they
look like.
// Account.cpp
...
void Account::open() {
string first_name;
string last_name;
cout << "\n*OPEN AN ACCOUNT*" << endl;
cout << "First Name: " << endl;
cin >> first_name;
cout << "Last Name: " << endl;
cin >> last_name;
long acct_amt;
cout << "Account Amount: " << endl;
cin >> acct_amt;
v_list.push_back(new Account("", "", 0));
v_list.back()->setFirstName(first_name);
v_list.back()->setLastName(last_name);
v_list.back()->setAccountAmount(acct_amt);
cout << *v_list.back() << endl;
// Save to a txt file
ofstream ofs("bank_ledger.txt", ios::app);
ofs << *v_list.back();
ofs.close();
}
Account *Account::searchByAccountNumber(const long &acct_num) {
vector<Account *>::iterator itr;
// https://stackoverflow.com/questions/15598607/when-should-i-use-stdbind#15598734
itr = find_if(v_list.begin(), v_list.end(),
[&](auto acct_ptr) { return compareAccountNumber(acct_ptr, acct_num); });
if (itr != v_list.end())
return *itr;
else {
Account *ptr = nullptr;
return ptr;
}
}
void Account::balance() {
long balance_account_number;
cout << "\n*BALANCE ENQUIRY*" << endl;
cout << "Enter Account Number: " << endl;
cin >> balance_account_number;
Account *balance_ptr = searchByAccountNumber(balance_account_number);
if (balance_ptr != nullptr)
cout << *balance_ptr << endl;
else
cout << "Account Not Found. " << endl;
}
void Account::ledgerDump() {
ofstream ofs("bank_ledger.txt", ios::trunc);
for (auto x : v_list)
ofs << *x;
ofs.close();
}
void Account::deposit() {
long deposit_account_number;
long deposit_amt;
cout << "\n*DEPOSIT*" << endl;
cout << "Enter Account Number: " << endl;
cin >> deposit_account_number;
Account *deposit_ptr = searchByAccountNumber(deposit_account_number);
if (deposit_ptr != nullptr) {
cout << *deposit_ptr << endl;
cout << "\nEnter Deposit Amount: " << endl;
cin >> deposit_amt;
deposit_ptr->setAccountAmount(deposit_amt + deposit_ptr->getAccountAmount());
cout << "Total Amount "
<< deposit_amt
<< " has been deposited into Account Number "
<< deposit_account_number
<< endl;
// Update the ledger file
ledgerDump();
cout << *deposit_ptr << endl;
} else
cout << "Account Not Found. " << endl;
}
void Account::withdraw() {
long withdraw_account_number;
long withdraw_amt;
cout << "\n*WITHDRAWAL*" << endl;
cout << "Enter Account Number: " << endl;
cin >> withdraw_account_number;
Account *withdraw_ptr = searchByAccountNumber(withdraw_account_number);
if (withdraw_ptr != nullptr) {
cout << *withdraw_ptr << endl;
cout << "\nEnter Withdrawal Amount: " << endl;
cin >> withdraw_amt;
withdraw_ptr->setAccountAmount(withdraw_ptr->getAccountAmount() - withdraw_amt);
cout << "Total Amount "
<< withdraw_amt
<< " has been withdrawn into Account Number "
<< withdraw_account_number
<< endl;
// Update the ledger file
ledgerDump();
cout << *withdraw_ptr << endl;
} else
cout << "Account Not Found. " << endl;
}
void Account::close() {
cout << "\n *CLOSE ACCOUNT* " << endl;
long close_account_number;
cout << "Enter Account Number: " << endl;
cin >> close_account_number;
Account *close_ptr = searchByAccountNumber(close_account_number);
if (close_ptr != nullptr) {
vector<Account *>::iterator iter;
for (iter = v_list.begin(); iter < v_list.end(); ++iter) {
if ((*iter)->getAccountNumber() == close_account_number) {
cout << **iter << endl;
v_list.erase(iter);
}
}
ledgerDump();
cout << "Account Number " << close_account_number
<< " has been closed." << endl;
} else
cout << "Account Not Found. " << endl;
}
void Account::showAll() {
cout << "\n*ALL ACCOUNTS*";
for (auto acct_ptr : v_list)
cout << *acct_ptr << endl;
}
...
The destructor and friend functions are listed below.
// Account.cpp
...
Account::~Account() = default;
ifstream const &operator>>(ifstream &ifs, vector<Account *> &v_list) {
long account_num;
string first_name;
string last_name;
long acct_amt;
ifs >> account_num >> first_name >> last_name >> acct_amt;
v_list.push_back(new Account(account_num, first_name, last_name, acct_amt));
return ifs;
}
ostream &operator<<(ostream &out, const Account &a) {
out << "\nAccount Number: " << a.getAccountNumber() << endl
<< "First Name: " << a.getFirstName() << endl
<< "Last Name: " << a.getLastName() << endl
<< "Account Amount: " << a.getAccountAmount();
return out;
}
const ofstream &operator<<(ofstream &ofs, const Account &a) {
ofs << "\n"
<< a.getAccountNumber() << endl
<< a.getFirstName() << endl
<< a.getLastName() << endl
<< a.getAccountAmount();
return ofs;
}
...
The complete code base can be found on my GitHub.
Stay tuned by signing up for my newsletter. If you have any questions/comments/proposals, feel free to shoot me a message on Twitter/ Discord/ Patreon.
Happy coding!

